Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Kimiaki
Genshiryoku No Ima To Ashita, p.148 - 151, 2019/03
no abstracts in English
Matsuzuru, Hideo
Nihon Gakujutsu Kaigi Kohaishita Seikatsu Kankyo No Sentan Gijutsu Ni Yoru Kaifuku Kenkyu Renrakukai Iinkai Shimpojiumu "Hoshasei Busshitsu Ni Yoru Kankyo Osen No Yobo Ni Mukete", p.53 - 62, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
Kanamori, Masashi
JNC TN8440 2001-018, 50 Pages, 2001/12
On September 30 at around 10:35 AM, criticality accident occurred at the JCO's conversion building in Tokai-mura. Since criticality accident had not been anticipated, neither devices for termination of criticality accident nor neutron detectors were available. Immediately after the information of the accident, our emergency staff (Japan Nuclear cycle development institute staff) went to JCO site, to measure the intensity of neutrons and gammas. There were four main tasks, first one was to measure the radiation intensity, second one was to terminate the criticality accident, third one is to alert the residents surrounding the JCO site, fourth one is to evacuate the employees in the site. These tasks were successfully performed until October 1. This paper describes about how these operations were performed by the relevant staffs.
Sakamoto, Ryuichi; Saito, Kimiaki; Tsutsumi, Masahiro; Nagaoka, Toshi
Hoken Butsuri, 36(4), p.297 - 307, 2001/12
There are many factors which affect external exposure in contaminated area: distributions of fallout, compositions of radioactive nuclides, soil conditions, depth profile of radioactivity in soil, rain fall, snow cover, radioactive decay, shielding effects of houses and other structures, de-contamination measures, and the 'occupancy factor' which accounts for the fraction of time that inhabitants spend in different locations. In this study, several important issues concerning these factors have been investigated using field measurements and computational simulations since 1992 in the Chernobyl area. The objectives of the study were: (1) The development of a mobile survey method to collect radiation data of the contaminated area over a wide area in a short time; (2) The verification of a method to infer external doses to the population; (3) The provision of basic data used for the evaluation of external dose due to gamma ray using a Monte Carlo simulation method. (4) Characteristics of the radiation fields in contaminated area. In this report, the results were summerized.
Shinohara, Kunihiko; Takeishi, Minoru; ; ; Mizutani, Tomoko
JNC TN8440 2001-019, 141 Pages, 2001/11
This report was written about the effluent control in JNC Tokai Works from 1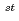 April 2000 to 31
April 2000 to 31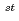 March 2001. In this period, the quantities and concentrations of retroactivities in liquid waste from Tokai Works were under the discharge limits of "Safety Regulations for the Tokai Reprocessing Plant", "Safety Regulations for the Tokai Reprocessing Plant" and regulations of government.
March 2001. In this period, the quantities and concentrations of retroactivities in liquid waste from Tokai Works were under the discharge limits of "Safety Regulations for the Tokai Reprocessing Plant", "Safety Regulations for the Tokai Reprocessing Plant" and regulations of government.
; ; ; Takeda, Seiichiro
JNC TN8420 2001-008, 134 Pages, 2001/07
This investigation was conducted as a part of planning the low-level radioactive waste management program (LLW management program). The aim of this investigation was contributed to compile the radioactive waste database of JNC's LLW management program. All nuclear facilities of the Tokai works and Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center were investigated in this work. The wastes generated by the decomissioning of each nuclear facility were classified into radioactive waste and others (exempt waste and non-radioactive waste), and the amount of the wastes was estimated. The estimated amounts of radioactive wastes generated by decomissioning of the nuclear facilities are as follows. (1)Tokai works. The amount of waste generated by decommissioning of nuclear facilities of the Tokai works is about 1,079,100 ton. The amount of radioactive waste is about 15,400 ton. The amount of exempt waste and non-radioactive waste is about 1,063,700 ton. (2)Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center. The amount of waste generated by decommissioning of nuclear facilities of Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center is about 112,500 ton. The amount of radioactive waste is about 7,800 ton. The amount of exempt waste and non-radioactive waste is about 104,700 ton.
Maruo, Yoshihiro; ; Takeishi, Minoru; ; ; Takeyasu, Masanori;
JNC TN8440 2001-011, 146 Pages, 2001/06
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed since 1975, based on "Safety Regulations for the Tokai Reprocessing Plant, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitants due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant during April 2000 to March 2001. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring program, monitoring results, meteorological data and annual discharges from the plant.
Shinohara, Kunihiko; ; ; ; ; Kano, Yutaka;
JNC TN8440 2001-004, 62 Pages, 2001/02
Concerming about the action for the criticality accident in JCO Co., Ltd. (JCO) occurred at 10:35 on 30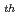 Sept. 1999, Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute(JNC) established "JNC's task force" at 12:35 on the same date in conjuction with Head Office and Tokai Works. And JNC's task force had supported the government of Japan, the local governments and JCO humanly, physically and technically until the jobs of the task force was transferred to "Support Assembly for Countermeasure and Research of JCO Criticality Accident" and routine line on 12
Sept. 1999, Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute(JNC) established "JNC's task force" at 12:35 on the same date in conjuction with Head Office and Tokai Works. And JNC's task force had supported the government of Japan, the local governments and JCO humanly, physically and technically until the jobs of the task force was transferred to "Support Assembly for Countermeasure and Research of JCO Criticality Accident" and routine line on 12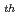 Oct. 1999. This report compiled the results of the environmental monitoring performed by JNC based on the request from the government of Japan and the local governments.
Oct. 1999. This report compiled the results of the environmental monitoring performed by JNC based on the request from the government of Japan and the local governments.
; Shinohara, Kunihiko; ; ; ; Takeyasu, Masanori;
JNC TN8440 2000-007, 141 Pages, 2000/06
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed since 1975, based on "Safety Regulations for the Tokai Reprocessing Plant, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitants due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant during April 1999 to March 2000. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring program, monitoring results, meteorological data and annual discharges from the plant.
*; Ijiri, Yuji*; *; *
JNC TN8400 2000-021, 66 Pages, 2000/04
A reliability evaluation for radionuclide transport analysis code, MATRICS, used in radionuclide transport analysis in the natural barrier system PA in H12 report has been carried out. Sensitivity analysis to radionuclide transport parameter in MATRICS and analytical solution has been performed, and the results of each analysis have been compared. Additionally sensitivity analysis using Talbot Method, Crump method and Hosono method has been carried out, and the results of each inverse Laplace transform method has been compared. The conclusions obtained from the results of the evaluation are summarized as follows, (1)In case of the infinite matrix diffusion distance, an error among the results of each calculation is maximum about 0.4% in the range of Pe number from 1.0 to 100. And, an error among the results of each calculation is maximum about 5.5% in the range of transmissivity from 1.0 10
10 to 1.0
to 1.0 10
10 (m
(m /s). (2)In case of the finite matrix diffusion distance (0.03
/s). (2)In case of the finite matrix diffusion distance (0.03 1.0(m)), an error among the results of each calculation is maximum about 0.7% in the range of Pe number from 1.0 to 100. And, an error among the results of each calculation is maximum about 2.4% in the range of transmissivity from 1.0
1.0(m)), an error among the results of each calculation is maximum about 0.7% in the range of Pe number from 1.0 to 100. And, an error among the results of each calculation is maximum about 2.4% in the range of transmissivity from 1.0 10
10 to 1.0
to 1.0 10
10 (m
(m /s). 3)By comparing Talbot method with other inverse Laplace transform method, Talbot method is confirmed to give similar results with other inverse Laplace transform method in the range of Pe number from 5.0
/s). 3)By comparing Talbot method with other inverse Laplace transform method, Talbot method is confirmed to give similar results with other inverse Laplace transform method in the range of Pe number from 5.0 10
10 to 2.0
to 2.0 10
10 , and that of transmissivity below 1.0
, and that of transmissivity below 1.0 10
10 (m
(m /s). Therefore, it is concluded that the reliability of MATRICS are confirmed by conducting sensitivity analysis in the range of Pe number and transmissivity coefficient used in H12 report.
/s). Therefore, it is concluded that the reliability of MATRICS are confirmed by conducting sensitivity analysis in the range of Pe number and transmissivity coefficient used in H12 report.
Moriyama, Hirotake*
JNC TJ8400 2000-050, 47 Pages, 2000/03
In support of the safety assessment of geologic disposal of high levcl radioactive wastes, the solubility of transuranium elements was studied. The solubility of PuO
 xH
xH O was measured undcr a reducing condition, and the solubility product K
O was measured undcr a reducing condition, and the solubility product K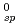 and the stability constant
and the stability constant 
 of Pu(OH)
of Pu(OH) were obtained. The obtained K
were obtained. The obtained K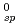 value was found to be much smaller than that predicted by Rai et al. from its dependence on ionic radius. Also, the solubility of PuO
value was found to be much smaller than that predicted by Rai et al. from its dependence on ionic radius. Also, the solubility of PuO 3
3  xH
xH O was measured under an oxidizing condition and the solubility product K
O was measured under an oxidizing condition and the solubility product K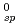 was obtained. In the analysis of hydrolysis constants of actinide ions, it was found that the systematic trend of the hydrolysis constants was well explained by the hard sphere model considering the effective charges of actinide ions.
was obtained. In the analysis of hydrolysis constants of actinide ions, it was found that the systematic trend of the hydrolysis constants was well explained by the hard sphere model considering the effective charges of actinide ions.
*; *; Morooka, Koichi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-043, 170 Pages, 2000/03
This study is an object to collect and arrange data about the mass transfer path during a natural barrier system by grasping actual rock feature, in order to be useful for a performance assessment of a natural barrier system at geological disposal of HLW. An existence of permeability high large-scale faults extends a large influence over a performance assessment of geological disposal. With "The Second Progress Report on Research and Development for the Geological Disposal of HLW in Japan" which Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) issued, it is as" A repository would be located at least 100 meters away from major faults and major fracture zones which could adversely affect the stability and performance of the repository" as a Reference Case concept model of a natural barrier system, Then, they are as "in the Reference Case, the transport path consists of the host rock and the downstream fault". It will not be easy to know the distribution of faults in the subsurface deep division without data acquired from many boreholes and underground laboratory. With this study, specific data on the large-scale faults and fracture zones has been collected and arranged by investigating in underground galleries and on the literatures of a post-operated mine site. Based on this result, a consideration on the principal transfer pass at a natural barrier system has been conducted. The contents conducted in this report is the follows. (1)investigation of literature about data of fracture, shear zone, and geology, (2)field investigation of fracture and shear zone in the rock, (3)arrangement of these results, (4)modeling of the major water conductive feature, and (5)evaluation of an assumption which has been introduced in the Second Progress Report issued by JNC.
Ikeda, Takao*; Yoshida, Hideji*; Miki, Takahito*
JNC TJ8400 2000-046, 264 Pages, 2000/02
This report contains discussions about methodology for the selection of parameter values, stochastic approach for the biosphere assessment and biosphere modelling for marine discharge case are described. Regarding the methodology for the selection of parameter values, important aspects for the data selection were discussed, and data selection protocol was developed. Regarding the stochastic approach for the biosphere assessment, it is confirmed that Straightforward Monte Carlo Method and Latin Hypercube Sampling Method are the most adequate based on a literature survey. Then stochastic assessment by using biosphere model that was developed in the second progress report was carried out to check the sensitivity of parameter values. Finally, availability of several kind of assessment models for marine discharge case were discussed. It was confirmed that Multiple Compartment Model was the most applicable. Assessment using Multiple Compartment Model was carried out. The results were compared with those derived by numerical model. As a result, the difference between two models were small enough.
Tochiyama, Osamu*
JNC TJ8400 2000-044, 53 Pages, 2000/02
To estimate the polyelectrolyte effect and the effect of the heterogeneous composition of humic acids, the complex formation constants of Eu(III) and Ca(II) with Aldrich humic acid and polyacrylic acid were obtained, for Eu(10 to 10
to 10 M) by solvent extraction with TTA and TBP in xylene, for Ca (10
M) by solvent extraction with TTA and TBP in xylene, for Ca (10 M) with TTA and TOPO in cyclohexane and for Ca(10
M) with TTA and TOPO in cyclohexane and for Ca(10 M) by using ion-selective electrode. By defining the apparent formation as
M) by using ion-selective electrode. By defining the apparent formation as  = [MR
= [MR ]/([M][R]), where [R] denotes the concentration of dissociated functional group, [M] and [MR
]/([M][R]), where [R] denotes the concentration of dissociated functional group, [M] and [MR ] denote the concentration of free and bound metal ion and pcH is defined as-log[H], the values of log
] denote the concentration of free and bound metal ion and pcH is defined as-log[H], the values of log have been obtained at pcH 4.8 - 5.5 in 0.1 - 1.0M NaClO
have been obtained at pcH 4.8 - 5.5 in 0.1 - 1.0M NaClO and NaCl. Log
and NaCl. Log of Eu-humate varied from 5.0 to 9.3 and that of Ca-humate from 2.0 to 3.4..For both humate and polyacrylate, log
of Eu-humate varied from 5.0 to 9.3 and that of Ca-humate from 2.0 to 3.4..For both humate and polyacrylate, log increased with pcH or with the degree of dissociation. The increase in the ionic strength O.1 to 1.0 M decreased the log
increased with pcH or with the degree of dissociation. The increase in the ionic strength O.1 to 1.0 M decreased the log , the decrease in log
, the decrease in log of Eu(III)-humate is 1.6, that of Eu(III), polyacrylate 0.7, that of Ca(II)-humate 1.9 and that of Ca(II)-polyacrylate 1.2. While the increase in the metal ion produced no effect on log
of Eu(III)-humate is 1.6, that of Eu(III), polyacrylate 0.7, that of Ca(II)-humate 1.9 and that of Ca(II)-polyacrylate 1.2. While the increase in the metal ion produced no effect on log of polyacrylate, log
of polyacrylate, log of humate decreased. Depending on the concentration of Eu(III), the coexistence of Ca(II) reduced log
of humate decreased. Depending on the concentration of Eu(III), the coexistence of Ca(II) reduced log  of humate by 0 to 0.8. The dependence of log
of humate by 0 to 0.8. The dependence of log of humate on the metal ion concentration suggests the coexistence of strong and weak binding sites in the hmnic acid.
of humate on the metal ion concentration suggests the coexistence of strong and weak binding sites in the hmnic acid.
Kudo, Akira*; Fujikawa, Yoko*
JNC TJ8400 2000-010, 67 Pages, 2000/02
The first and second environmental releases of man-made  Pu came from nuclear explosions at Alamagordo and Nagasaki in 1945. The release at Nagasaki was more serious than at Alamagordo, because it happened in an area with a high population density. Unfissioned
Pu came from nuclear explosions at Alamagordo and Nagasaki in 1945. The release at Nagasaki was more serious than at Alamagordo, because it happened in an area with a high population density. Unfissioned  Pu and various fission products have been interacting here with various environmental materials (soils, sediments, and plants) under wet and temperature conditions for more than 45 years. To assess the environmental mobility of
Pu and various fission products have been interacting here with various environmental materials (soils, sediments, and plants) under wet and temperature conditions for more than 45 years. To assess the environmental mobility of  Pu, the distributions of radionuclides from this release were investigated at Nishiyama where heavy black rain containing unfissioned plutonium and fission products fell 30 minutes after the nuclear explosion. The vertical distributions of
Pu, the distributions of radionuclides from this release were investigated at Nishiyama where heavy black rain containing unfissioned plutonium and fission products fell 30 minutes after the nuclear explosion. The vertical distributions of  Cs and
Cs and  Pu were determined in unsaturated soil cores up to 450cm deep. Most radionuclides were found in the soil column 30cm from the ground surface. However,
Pu were determined in unsaturated soil cores up to 450cm deep. Most radionuclides were found in the soil column 30cm from the ground surface. However,  Pu were detected in the groundwater as well below a depth of 200cm. No
Pu were detected in the groundwater as well below a depth of 200cm. No  Cs was found below 40cm from the ground surface or in groundwater. These observations reveal that about 3% of the total
Cs was found below 40cm from the ground surface or in groundwater. These observations reveal that about 3% of the total  Pu have been migrating in the soil at a faster rate than the remaining
Pu have been migrating in the soil at a faster rate than the remaining  Pu. Sharp peak of
Pu. Sharp peak of  Cs and
Cs and  Pu, indicating heavy deposition from the Nagasaki local fallout of 1945, were found in sediment cores collected from the Nishiyama reservoir.
Pu, indicating heavy deposition from the Nagasaki local fallout of 1945, were found in sediment cores collected from the Nishiyama reservoir.  Pu peaks were unexpectedly discovered in pre-1945 sediment core sections. NO
Pu peaks were unexpectedly discovered in pre-1945 sediment core sections. NO  Cs was found. By contrast to the distribution in sediment cores,
Cs was found. By contrast to the distribution in sediment cores,  Cs in tree rings had spread by diffusion from the bark to the center of the tree without holding a fallout deposition record. Most of the
Cs in tree rings had spread by diffusion from the bark to the center of the tree without holding a fallout deposition record. Most of the  Pu was distributed in the tree rings following a similar deposition record to that found in sediment cores. Furthermore, a very small amount of
Pu was distributed in the tree rings following a similar deposition record to that found in sediment cores. Furthermore, a very small amount of  Pu (about 1%) was found unexpectedly in pre-1945 tree rings. The only reasonable ...
Pu (about 1%) was found unexpectedly in pre-1945 tree rings. The only reasonable ...
Ota, Kunio; Nakano, Katsushi; Metcalfe, R.; Ikeda, Koki; ; Amano, Kenji; Takeuchi, Shinji; Hama, Katsuhiro; Matsui, Hiroya
JNC TN7410 99-007, 44 Pages, 1999/08